Navigating Medical Device Regulations in Hong Kong: A Simple Guide
Ever wondered how medical devices in Hong Kong get to be used safely in hospitals and clinics? It's a journey that involves strict rules and careful oversight. To our understanding, ensuring these devices are safe, effective, and high-quality is paramount for patient well-being here in Hong Kong. We've seen firsthand how crucial a robust system is, and that's exactly what Hong Kong has built with its Medical Device Control System (MDACS).
What's the Deal with Medical Device Regulations in Hong Kong?
From our experience, many people find "regulations" a bit daunting. But think of it this way: these rules are in place to protect you and your loved ones when you interact with medical devices.
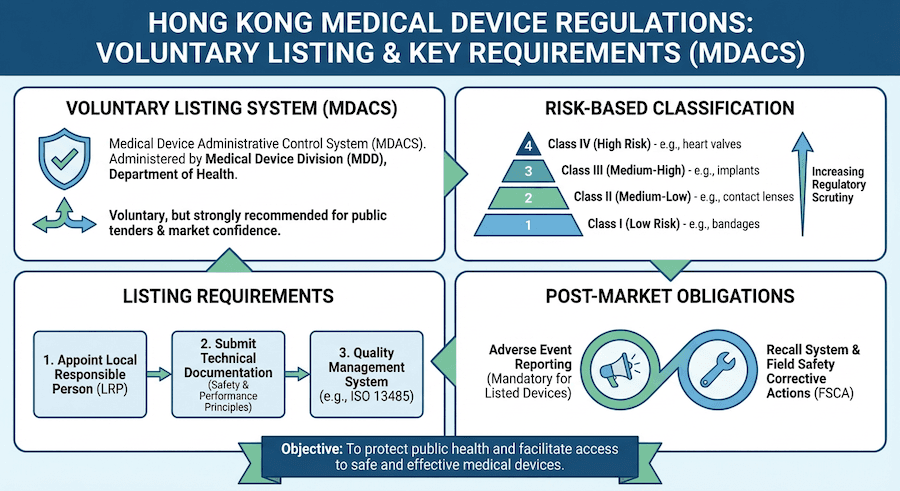
So, who's in charge of all this? According to our knowledge, it's primarily the Department of Health, specifically their Medical Device Control Office. They run the show under the Medical Device Administrative Control System (MDACS), which is the cornerstone of medical device oversight here.
The Ground Rules: Key Legislation
We've found that understanding the basic laws helps. Here are the main ones we typically refer to:
- Medical Device Administrative Control System (MDACS): This is the big one, the backbone of regulation.
- Import and Export Ordinance (Cap. 60): As you can imagine, bringing devices into Hong Kong needs proper procedures.
- Trade Descriptions Ordinance (Cap. 362): This ensures that what a device claims to do is actually true – no misleading information allowed!
- Consumer Goods Safety Ordinance (Cap. 456): Even though medical devices have their own specific rules, this general safety ordinance helps ensure consumer protection.
Who's Who in the Regulatory World?
When we talk about the regulatory landscape, several key players are involved:
- Department of Health (Medical Device Control Office): These are the main folks you'll interact with.
- Medical Device Advisory Committee: Think of them as the expert panel offering guidance.
- Technical Review Committees: These groups dive into the nitty-gritty technical details of devices.
- Inspection and Enforcement Units: They're on the ground, making sure everyone's playing by the rules.
How Are Medical Devices Classified? It's All About Risk!
Have you ever thought about why some medical devices are treated differently than others? From our perspective, it all comes down to risk. Imagine a simple bandage versus a pacemaker – the potential impact on a patient is vastly different! Hong Kong's system classifies devices based on their risk level.
The "Risk Ladder": Our Classification System
To our understanding, devices are categorized into four classes, like steps on a ladder, from lowest to highest risk:
- Class I: Low-risk devices. Think everyday items.
- Class II: Medium-risk devices. A bit more involved.
- Class III: Medium-high risk devices. Getting serious now.
- Class IV: High-risk devices. These are the ones that need the most careful scrutiny.
What Makes a Device "Risky"? Key Criteria We Look At:
When we assess a device's classification, we consider things like:
- How long does it touch your body? A quick touch versus something implanted for years.
- How invasive is it? Does it just sit on your skin, or does it go inside your body?
- Does it affect just one spot, or your whole system?
- Is it "active" (needs power) or "non-active"?
- Where in the body is it used? Critical areas like the heart or brain demand extra care.
Getting Your Medical Device Registered: What You Need to Know
Is every medical device in Hong Kong registered? Not necessarily! Based on our experience, while the MDACS system is voluntary, certain devices absolutely need to be registered to be legally marketed and used here.
Must-Register Devices Under MDACS:
If you're dealing with these types of devices, registration is typically a must:
- Class II, III, and IV devices: As we discussed, these are the medium to high-risk ones.
- In vitro diagnostic devices: Think lab tests and diagnostic kits.
- Active implantable devices: Like pacemakers, these go inside the body and need power.
- Sterile devices: Any device that needs to be completely free of germs for its intended use.
- Devices with measuring functions: Think thermometers or blood pressure monitors – accuracy is key!
Devices That Might Be Exempted:
On the other hand, some devices might get a pass from mandatory registration:
- Class I non-sterile devices: Simple, low-risk items that don't need to be sterile.
- Custom-made devices: Unique devices made for a specific patient.
- Devices for clinical investigation: Those being tested in trials.
- Certain traditional devices: Some older, well-established types.
- Emergency use devices: Those used in urgent situations where immediate access is critical.
The Registration Journey: A Step-by-Step Look
So, you've got a device that needs registering. What's the process like? From our perspective, it involves a few key stages.
Before You Submit: Getting Ready
Think of these as your preparation steps, essential for a smooth application:
- Figure out your device's class: This is the very first step, and as you know, it determines much of what comes next.
- Set up your quality management system: We can't stress this enough – a robust quality system, like ISO 13485, is fundamental.
- Gather clinical evidence: Do you have data proving your device works and is safe?
- Prepare technical documents: All the specifications, designs, and test results.
- Appoint an authorized representative: You'll need a local contact to handle things in Hong Kong.
What to Submit: The Application Checklist
When you're ready to submit, here's what you'll typically need to include:
- The official application form and fees.
- A clear device description and specifications.
- Quality management certificates, proving your system is up to par.
- Clinical evaluation reports, showing the evidence of safety and performance.
- Labeling and instructions for use – these must be clear and compliant.
Diving into the Technical Bits: Documentation and Quality
When it comes to medical devices, details matter. A lot. To our understanding, the technical documentation and quality management systems are where the rubber meets the road.
What Does "Technical Documentation" Even Mean?
In simple terms, it's the complete story of your device, on paper. It answers all the "how" and "why" questions. Key things we look for include:
- Device design and manufacturing details: How was it made? What materials were used?
- Risk management documentation: How have you identified and managed potential risks?
- Clinical evaluation data: The proof that it's safe and effective.
- Post-market surveillance plans: How will you keep an eye on it once it's out there?
- Quality management system certificates: Evidence of your robust quality processes.
Supporting Your Claims: Important Documents
Beyond the core documents, you'll often need supporting paperwork:
- ISO 13485 certificates: A globally recognized standard for medical device quality.
- Test reports and certificates: Proof that your device meets various safety and performance standards.
- Clinical study reports: Detailed findings from any trials.
- Literature reviews: What does existing research say about similar devices?
- Predicate device comparisons: How does your device stack up against similar, already approved devices?
Quality Management Systems: The Foundation of Trust
What's a Quality Management System (QMS)? Simply put, it's how a company ensures its products consistently meet requirements and customer satisfaction. For medical devices, this is absolutely critical. Our experience tells us that a strong QMS, particularly one aligned with ISO 13485, is non-negotiable.
The Pillars of ISO 13485: What We Focus On
This international standard guides how medical device companies should operate. It covers areas like:
- Management responsibility: Leadership commitment to quality.
- Resource management: Having the right people and tools.
- Product realization: From design to manufacturing.
- Measurement and improvement: Constantly checking and getting better.
- Risk management integration: Building risk control into everything.
Getting Certified: The Role of Certification Bodies
You don't just "say" you have a QMS; you get it certified. This typically involves:
- Notified bodies recognition: Working with approved organizations.
- Accreditation requirements: Meeting specific standards for certification.
- Surveillance audits: Regular check-ins to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Certificate maintenance: Keeping your certification current.
- Non-conformity management: What happens when something goes wrong? How do you fix it?
Clinical Evidence: Proving Your Device Works (and is Safe!)
How do we know a medical device is actually going to help, not harm? This is where clinical evidence comes in. From our understanding, this is essentially the scientific proof that your device does what it's supposed to and is safe for patients.
How We Evaluate Clinical Evidence
We look at various ways to gather this crucial information:
- Literature review: What do scientific studies already say about similar devices or technologies?
- Clinical investigations: Running studies with real patients.
- Post-market clinical follow-up: Continuing to gather data after the device is on the market.
- Equivalence demonstrations: Showing your device is just as good as one that's already proven.
- Risk-benefit analysis: Weighing the potential benefits against any possible risks.
Getting Serious with Clinical Investigations
If a clinical investigation is needed, there are strict rules to follow:
- Protocol development: A clear plan for the study.
- Ethics committee approval: Ensuring the study is ethical and protects patients.
- Investigator qualifications: Making sure the people running the study are qualified.
- Good Clinical Practice (GCP) compliance: Following international standards for clinical trials.
- Safety reporting: Immediately reporting any unexpected issues.
Labeling Your Device: What Needs to Be Said?
Ever picked up a product and wondered what all those tiny words mean? For medical devices, every word on that label is critical. To our understanding, clear and comprehensive labeling is essential for both users and patients.
What Information is a Must-Have?
When we talk about medical device labeling, these are the key pieces of information you can't skip:
- Device name and model: Simple identification.
- Manufacturer information: Who made it?
- Intended use and indications: What is it for? Who should use it?
- Contraindications and warnings: When not to use it, and what dangers to watch out for.
- Instructions for use: How do you actually use it safely and effectively?
Language and Look: What Else Do We Consider?
Beyond the words, there are other important aspects:
- English labeling mandatory: It's the standard.
- Chinese translation recommended: To serve the local population better, it's always a good idea to include Chinese.
- Symbol usage standards: Recognized symbols can convey information quickly.
- Font size requirements: Can people actually read it?
- Durability specifications: Will the label last as long as the device?
After the Sale: Post-Market Surveillance
Just because a medical device is on the market doesn't mean the oversight stops. In fact, according to our experience, post-market surveillance is a continuous and vital part of ensuring ongoing safety and quality. Think of it as a safety net.
The "Watchdog" System: Vigilance
This system is all about keeping an eye on devices once they're out in the real world:
- Adverse event reporting: If something goes wrong, it needs to be reported.
- Field safety corrective actions: If a widespread issue is found, what steps are taken to fix it?
- Periodic safety update reports: Regular updates on the device's safety profile.
- Risk management updates: Constantly reassessing and managing risks.
- Market surveillance activities: Proactively looking for issues.
Reporting Issues: Our Obligations
We all have a role to play in reporting problems. Here's a quick look at reporting timelines we typically adhere to:
- Any adverse events that have posed or are likely to pose a public health risk: 48 hrs
- Any adverse events that have resulted in death or serious injury: 10 days
- All other reportable adverse events: 30 days
- Follow-up final report: within 30 elapsed calendar days of the initial reports
Getting Devices into Hong Kong: Import and Distribution
So, a device is approved – how does it actually get into the country and to the right people? This involves specific import and distribution rules. To our understanding, these steps ensure the integrity of the medical device supply chain.
Bringing Devices In: Import Requirements
If you're importing medical devices, you'll generally need:
- Medical device trader license
- Import permits
- Customs declarations
- Quality certificates
- Storage and handling protocols
Getting Devices to Users: Distribution Controls
Once devices are in Hong Kong, how they're distributed is also regulated:
- Authorized distributors
- Supply chain integrity
- Storage conditions
- Recall procedures
- Traceability systems
Special Cases: IVD Devices, Software, and Combination Products
Not all medical devices are the same, and some have unique considerations. From our experience, these categories often require a deeper dive.
In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Devices: The Lab Test World
Think of IVDs as the tools used to diagnose conditions from samples like blood or urine. They have their own set of requirements:
- Performance evaluation: Does it accurately detect what it's supposed to?
- Analytical performance: How well does it measure what it's supposed to measure?
- Clinical performance: How well does it perform in a real-world clinical setting?
- Quality control materials: How do you ensure consistent results?
- Reference standards: What are the benchmarks for accuracy?
Classification Criteria for IVDs (Often Specific):
- Self-testing devices
- Near-patient testing
- High-risk analytes
- Blood grouping devices
- Infectious disease testing
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD): Apps and Algorithms
Did you know software can be a medical device? Absolutely! To our understanding, as technology evolves, so do the regulations.
Regulatory Approach for SaMD:
- Software classification: Just like physical devices, software is classified by risk.
- Cybersecurity requirements: Protecting patient data and device functionality is paramount.
- Validation and verification: Does the software do what it's designed to do, reliably?
- Change control procedures: How are updates and modifications handled?
- Post-market monitoring: Keeping an eye on software performance after release.
Essential Documentation for SaMD:
- Software lifecycle processes
- Risk management files
- Clinical evaluation
- Usability engineering
- Cybersecurity documentation
Combination Products: When Devices Mix with Other Things
Sometimes a medical device isn't just a device. It might be combined with a drug or a biological product. These are called combination products.
Drug-Device Combinations:
- Primary mode of action: Is it primarily a drug or a device? This determines the main regulatory pathway.
- Regulatory pathway determination
- Integrated review process: Often, both drug and device aspects are reviewed together.
- Quality requirements
- Clinical evaluation
Biological-Device Combinations:
- Component interaction: How do the biological and device parts work together?
- Manufacturing controls
- Sterilization validation
- Biocompatibility testing: Does the device interact safely with biological materials?
- Clinical assessment
International Harmony and Future Trends
Is Hong Kong an island when it comes to medical device regulations? Not at all! From our understanding, there's a strong push for international cooperation and keeping up with the latest advancements.
Global Harmony: Working Together
We've seen Hong Kong actively participate in global efforts to align regulations:
- International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF): A key group promoting global convergence.
- ISO standards adoption: Using internationally recognized standards.
- Mutual recognition agreements: Recognizing approvals from other trusted countries.
- Regulatory convergence
- Best practices sharing
Regional Cooperation:
- APEC harmonization
- ASEAN medical device directive
- Bilateral agreements
- Information exchange
- Joint inspections
What's Next? Emerging Technologies
The medical world is constantly innovating, and regulations need to keep pace. We're seeing a lot of focus on:
- Digital Health:
- Mobile medical applications (apps): Can your phone become a medical tool?
- Artificial intelligence (AI) devices: AI assisting in diagnosis or treatment.
- Telemedicine platforms: Remote healthcare solutions.
- Wearable devices
- Remote monitoring systems
- Advanced Therapies:
- Regenerative medicine products: New ways to heal and repair the body.
- Gene therapy devices
- Cell therapy systems
- Tissue engineering products
- Personalized medicine devices: Tailored treatments for individuals.
Staying Compliant and the Costs Involved
Compliance isn't just a suggestion; it's a necessity. From our experience, staying on top of regulations is crucial to avoid issues. And yes, there are costs involved.
Inspections and Enforcement: Keeping Everyone Honest
The authorities conduct various checks to ensure compliance:
- Manufacturing facility inspections: Visiting where devices are made.
- Distributor audits: Checking how devices are stored and distributed.
- Market surveillance: Monitoring products already on the market.
- Complaint investigations
- Post-market studies
If issues are found, there can be serious consequences:
- Warning letters
- Product recalls
- License suspension
- Criminal prosecution
- Administrative penalties
What About the Money? Cost Considerations
We often get asked about the costs. It's not just about registration fees:
- Registration Fees: Application fees, annual fees, variation fees, inspection fees, certification costs.
- Compliance Costs:
- Implementing a robust quality system.
- Conducting clinical studies.
- Preparing all that technical documentation.
- Ongoing post-market surveillance.
- Hiring regulatory consulting (like us!).
Innovation and Support: Building a Healthier Future
While regulations are strict, Hong Kong also supports innovation. From our understanding, there are pathways to help new, breakthrough technologies reach patients faster.
Fast Track for Breakthroughs:
For truly innovative devices, there can be expedited processes:
- Breakthrough device designation: Special status for cutting-edge tech.
- Priority review pathways: Faster assessment.
- Expedited approval
- Conditional approvals
- Emergency use authorizations
Supporting the Industry:
The Department of Health also offers resources to help companies navigate the system:
- Pre-submission meetings: Getting early feedback on your application.
- Guidance documents: Clear instructions on what's required.
- Training programs
- Industry associations
- Regulatory sandboxes
Best Practices and Common Challenges (and How We Tackle Them!)
What's the secret to success in Hong Kong's medical device landscape? In our experience, it comes down to smart strategy and proactive quality management.
Our Recommended Best Practices:
- Regulatory Strategy:
- Early engagement: Don't wait until the last minute to think about regulations.
- Comprehensive planning: Map out your entire journey.
- Risk assessment: Understand and mitigate potential problems.
- Quality by design: Build quality into your device from the very beginning.
- Lifecycle management
- Quality Management:
- Continuous improvement: Always look for ways to get better.
- Risk-based thinking: Focus resources where risks are highest.
- Process optimization
- Competency development
- Customer focus
Facing the Hurdles: Common Challenges We See
We often encounter these issues with our clients:
- Classification uncertainties: Sometimes it's tough to figure out exactly which class a device falls into.
- Clinical evidence requirements: Gathering enough robust data can be a big ask.
- Technical documentation: The sheer volume and detail required can be overwhelming.
- Regulatory timelines: Things can take longer than expected.
- Cost management: Keeping expenses under control throughout the process.
Our Solutions to These Challenges:
Based on our experience, here's how we typically help overcome these hurdles:
- Expert consultation: Getting specialized advice from the start.
- Regulatory intelligence: Staying updated on the latest changes.
- Strategic planning: Having a clear roadmap.
- Quality systems: Investing in strong internal processes.
- Stakeholder engagement: Working closely with all parties involved.
Conclusion: Making Sense of Medical Device Regulations in Hong Kong
To our understanding, Hong Kong's system for medical device regulation is a well-thought-out framework designed to keep patients safe while still encouraging new, innovative technologies. It might seem complex at first, but with a clear understanding of the requirements, a commitment to quality, and perhaps a little expert guidance, navigating it successfully is absolutely achievable.
Anonymous
Our SaMD (Software as a Medical Device) performs diagnostic image analysis but does not directly control any hardware. Following the September 2025 update to TR-007, how does the MDD now interpret Classification Rule 12 for standalone software that lacks a 'direct medical purpose' in isolation but is intended for use with a specific imaging modality? Does this automatically trigger a Class II listing even if the software is technically 'standalone'?