Need Regulatory Help? Try Our Platform
Post your regulatory questions or request quotations from verified pharmaceutical consultants worldwide. Get matched with experts who specialize in your market.
January 15, 2025
Approximately 5 minutes
Pharmacy vs Medicine Store: Understanding the Key Differences
Pharmacy vs Medicine Store: Understanding the Key Differences
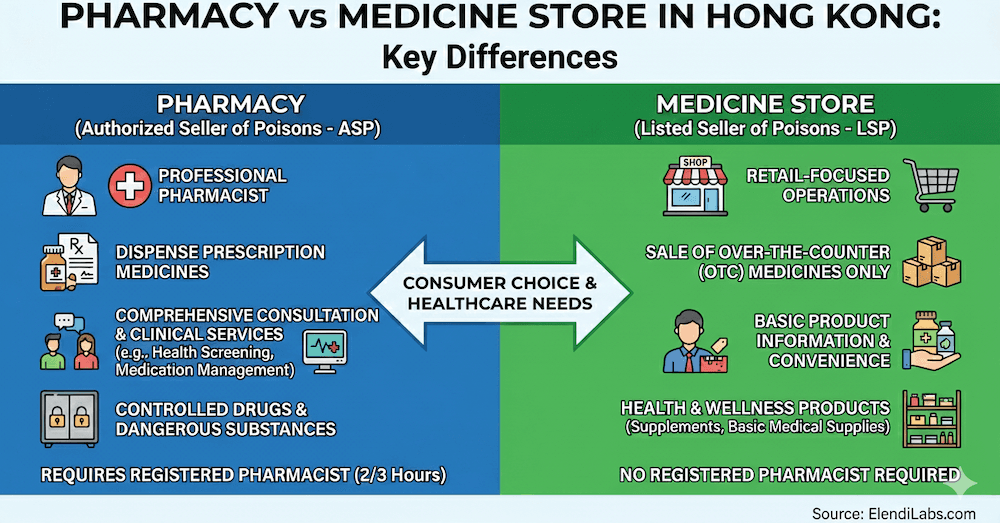
In Hong Kong's healthcare landscape, the terms "pharmacy" and "medicine store" are often used interchangeably by the public, but they represent distinctly different types of establishments with varying regulatory requirements, service capabilities, and operational scopes.
What is a Pharmacy?
A pharmacy is a healthcare facility operated under an Authorized Seller of Poisons (ASP) license, providing comprehensive pharmaceutical services including prescription dispensing and professional consultation.
Key Characteristics of Pharmacies:
Professional Services:
- Prescription medication dispensing
- Pharmaceutical consultation and counseling
- Medication therapy management
- Drug interaction screening
- Health screening services
- Vaccination services (where applicable)
Personnel Requirements:
- Must have a registered pharmacist present during 2/3 of operating hours
Inventory and Products:
- Part 1 and Part 2 poisons (prescription and over-the-counter medicines)
- Dangerous drugs
- Psychotropic substances
- Medical devices and health products
- Pharmaceutical-grade supplements
- Professional healthcare equipment
What is a Medicine Store?
A medicine store operates under a Listed Seller of Poisons (LSP) license, focusing primarily on retail sales of over-the-counter medicines and health products without prescription dispensing capabilities.
Key Characteristics of Medicine Stores:
Limited Services:
- Sale of over-the-counter medicines only
- Basic product information provision
- No prescription dispensing
- No professional pharmaceutical consultation
- Retail-focused operations
Personnel Requirements:
- No registered pharmacist required
- Basic training on product knowledge
Inventory and Products:
- Part 2 poisons and non-poisons only (over-the-counter medicines)
- Health and wellness products
- Dietary supplements
- Personal care items
- Basic medical supplies
Regulatory Framework Comparison
Licensing Requirements
Pharmacy (ASP License):
- Comprehensive application process
- Premises inspection by Pharmacy and Poisons Board
- Registered pharmacist employment
- Compliance with Good Pharmacy Practice standards
- Higher licensing fees and ongoing obligations
- Regular regulatory inspections
Medicine Store (LSP License):
- Simplified application process
- Basic premises requirements
- No pharmacist requirement
- Lower regulatory burden
- Reduced licensing fees
- Periodic compliance checks
Legal Obligations
Pharmacy Obligations:
- Prescription record keeping (minimum 7 years)
- Dangerous drug register maintenance
- Psychotropic substances register maintenance
- Part 1 Schedule 1 poisons register maintenance
- Adverse event reporting
Medicine Store Obligations:
- Sales record keeping
- Product storage compliance
- Customer information provision
- Inventory tracking
Service Scope Differences
What Pharmacies Can Do:
- Dispense prescription medications
- Provide medication counseling
- Conduct drug utilization reviews
- Offer immunization services
- Perform health screenings
What Medicine Stores Can Do:
- Sell over-the-counter medicines
- Provide basic product information
- Recommend suitable OTC products
- Offer health and wellness products
- Provide customer education on product use
- Maintain product availability
What Medicine Stores Cannot Do:
- Dispense prescription medications
- Provide professional pharmaceutical consultation
- Offer clinical services
- Recommend prescription alternatives
- Provide medication therapy management
- Conduct health assessments
Consumer Perspective
When to Visit a Pharmacy:
- Prescription medication needs
- Professional medication advice
- Drug interaction concerns
- Complex health conditions
- Medication management services
When to Visit a Medicine Store:
- Over-the-counter medication needs
- General health products
- Convenience shopping
- Basic health and wellness items
Business Operations
Pharmacy Operations:
- Higher operational complexity
- Professional service focus
- Prescription processing systems
- Clinical documentation requirements
- Insurance billing capabilities
- Specialized inventory management
Medicine Store Operations:
- Retail-focused operations
- Simpler inventory systems
- Customer service emphasis
- Commercial product focus
- Point-of-sale efficiency
- Marketing and promotion activities
Quality Assurance
Pharmacy Quality Standards:
- Temperature monitoring systems
- Professional quality reviews
- Medication error prevention
Medicine Store Quality Standards:
- Product integrity maintenance
- Expiry date monitoring
- Basic quality controls
Economic Considerations
Pharmacy Investment:
- Higher startup costs
- Pharmacist employment costs
- Professional equipment needs
- Compliance system requirements
- Insurance and liability costs
Medicine Store Investment:
- Lower startup costs
- Reduced staffing requirements
- Basic equipment needs
- Simpler compliance systems
Market Positioning
Pharmacy Market Position:
- Healthcare service provider
- Professional consultation focus
- Prescription medication specialist
- Patient care emphasis
- Healthcare partner role
Medicine Store Market Position:
- Retail convenience provider
- Product availability focus
- Cost-competitive positioning
- Accessibility emphasis
- Customer convenience
Regulatory Compliance
Pharmacy Compliance Requirements:
- Pharmacist supervision compliance
- Prescription handling procedures
- Regulatory reporting obligations
Medicine Store Compliance Requirements:
- Product handling standards
- Storage condition compliance
- Basic record keeping
Future Trends and Considerations
Pharmacy Evolution:
- Expanded clinical services
- Digital health integration
- Patient-centered care models
- Technology-enhanced services
Medicine Store Evolution:
- E-commerce integration
- Health and wellness expansion
- Convenience service enhancement
- Digital customer engagement
Choosing the Right Business Model
Consider a Pharmacy If:
- You want to provide comprehensive pharmaceutical services
- Professional healthcare delivery is your focus
- You have access to qualified pharmacists
- You can invest in comprehensive compliance systems
- Clinical services are part of your business model
- You want to build long-term patient relationships
Consider a Medicine Store If:
- Retail convenience is your primary focus
- You want lower operational complexity
- Limited initial investment is preferred
- Over-the-counter products meet your market needs
- Quick customer transactions are prioritized
- Commercial retail experience is your strength
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between pharmacies and medicine stores is crucial for both consumers and entrepreneurs in Hong Kong's healthcare sector. While pharmacies offer comprehensive pharmaceutical services with professional oversight, medicine stores provide convenient access to over-the-counter healthcare products.
Both models serve important roles in Hong Kong's healthcare ecosystem, providing different levels of service to meet diverse consumer needs.
For guidance on choosing the right pharmaceutical business model and navigating regulatory requirements, contact ElendiLabs for expert consultation.
Ask Anything
We'll follow up with you personally.
Related Articles
Approximately 5 minutes
Pharmacy vs Medicine Store: Understanding the Key Differences
Learn the crucial differences between pharmacies and medicine stores in Hong Kong, including licensing requirements, services offered, and regulatory distinctions.
Approximately 5 minutes
ASP vs LSP License: Which One Do You Need?
Learn the differences between Authorized Seller of Poisons (ASP) and Listed Seller of Poisons (LSP) licenses and determine which is right for your business.
Approximately 5 minutes
Professional Guide: Registration of Pharmaceutical Products and Substances in Hong Kong
A comprehensive guide for healthcare professionals and industry stakeholders on the registration requirements, procedures, and compliance for pharmaceutical products and substances in Hong Kong.